Transportation planning is dynamic, evolving with the communities it serves. A common industry approach to this need to evolve is continuous improvement—adding new data sources to models and refining forecast methods for greater visibility into potential future outcomes.
This process of refinement mirrors system dynamics thinking, which views the world as a complex, interlinked system, not as isolated activities. This perspective underscores the value of strategic modeling tools, which help users understand the complexities and connections within our transportation systems. These tools are designed to evaluate interactions between factors selected by users and not be overly fit to a specific set of inputs.
System dynamics thinking enables practitioners to come to terms with the complexity of transportation networks. Evaluating travel behavior is more than looking at demand along specific travel corridors. It is influenced by land-use patterns, demographic changes, economic conditions, ability and willingness to pay, and technological and social advances. These elements are interconnected, shaping travel demand and behaviors over time.
Adopting a system dynamics viewpoint reveals the interactions and feedback mechanisms affecting travel behaviors. It encourages looking beyond immediate challenges to consider the future impact of today’s decisions. VisionEval stands out as a crucial tool in this regard, providing the depth, foresight, and comprehensive understanding needed to develop future-focused solutions.
Advantages of System Dynamics Thinking
System dynamics thinking aids in developing policies that are both resilient and flexible. Scenario planning, supported by tools like VisionEval, allows for the visualization of numerous potential futures and the identification of shared solutions across them, offering multiple benefits to practitioners.
Integrating Diverse Factors
Transportation planning is not an isolated activity. Metropolitan planning organizations, for example, must align their long-range plans with local or state-wide goals. These goals can include reducing vehicle miles traveled (VMT), greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions, or crashes and serious injuries as well as improving transportation health outcomes. System dynamics thinking prompts practitioners to consider a mix of economic, environmental, and social factors, offering a wider view of possible futures. This is crucial for evaluating GHG emissions impacts, for instance, and a primary reason why the Federal Highway Administration (FHWA) recommends VisionEval to help with achieving emission reduction targets.
Gaining a Holistic Understanding
A system dynamics approach illuminates connections and mutual influences among policies or actions over time, delivering an informed perspective. It equips agencies with the ability to foresee how today’s decisions on infrastructure, policies, community needs, or technological innovations will affect future mobility, leading to plans that are resilient, adaptable, and in line with overarching goals.
Developing a Long-Term Perspective
System dynamics solutions, applied through tools like VisionEval, deliver foresight that is not only relevant in the short term but also remains accurate over longer spans. It encourages the consideration of long-term trends in demographics, technology, climate, and more, enabling the creation of forward-thinking strategies. By modeling various possible futures, it is possible to identify “signpost” performance measures. Such measures may help guide decision-makers as to which future they are heading toward and determine if a change in policy or investment may direct them toward a more desirable future state.
Supporting Informed Decision Making
System dynamics thinking underpins informed decision-making under deep uncertainty (DMDU) by offering a dynamic and detailed model of the outcomes from various planning or policy choices. It enables the evaluation of the effects of different scenarios, from infrastructure investments and technological developments to policy adjustments and beyond.

VisionEval: Bridging the Gap Between Long-Range Planning and Specific Projects
VisionEval is unique among strategic models. It is an open-source, travel demand tool that moves beyond traditional methods by integrating system dynamics thinking into its architecture. Designed to address the contemporary challenges of transportation planning, VisionEval introduces an inventive and adaptable way to examine various future scenarios.
The model uses an econometric approach using a disaggregate household population to predict household travel by considering a range of factors. This approach allows for a wide range of futures to be tested by varying the factors influencing demand along with changes in the transportation system and applicable policies.
As leaders in the development and application of VisionEval, RSG has helped agencies across the United States leverage its comprehensive capabilities for diverse scenario planning efforts. What distinguishes VisionEval from conventional transportation planning tools is its ability to deliver a more nuanced understanding of how multiple variables interact over time, facilitating informed decision-making for future transportation needs.
The VisionEval Difference
Traditional models typically focus on trip-based estimations, analyzing travel by mapping individual journeys from origin to destination. In contrast, VisionEval adopts a broader, more nuanced perspective by simulating daily activity patterns of household members. It integrates demand from demographic and socioeconomic data from a synthetic population with an aggregate representation of system supply.
VisionEval’s design and functionality offer several key benefits:
- Synthetic Population Modeling: This feature creates simulations with representations of individuals and households that mirror the complexity and diversity of real-world populations. Such detailed insights are essential for developing tailored policies and solutions that are effective, equitable, and sustainable.
- Incorporation of Multiple Factors: VisionEval facilitates the inclusion of environmental, economic, and social factors in its analyses. As these considerations become increasingly important to policymakers and transportation agencies, VisionEval’s ability to incorporate them into planning processes ensures that transportation systems are designed to be both environmentally sustainable and equitable for all users.
- Flexible Scenario Analysis: The tool enables users to navigate the uncertainties of future transportation developments by examining a wide range of potential scenarios. This capability allows agencies to identify strategies that support more likely positive outcomes in various future contexts, thereby selecting the most favorable path forward given the present conditions.
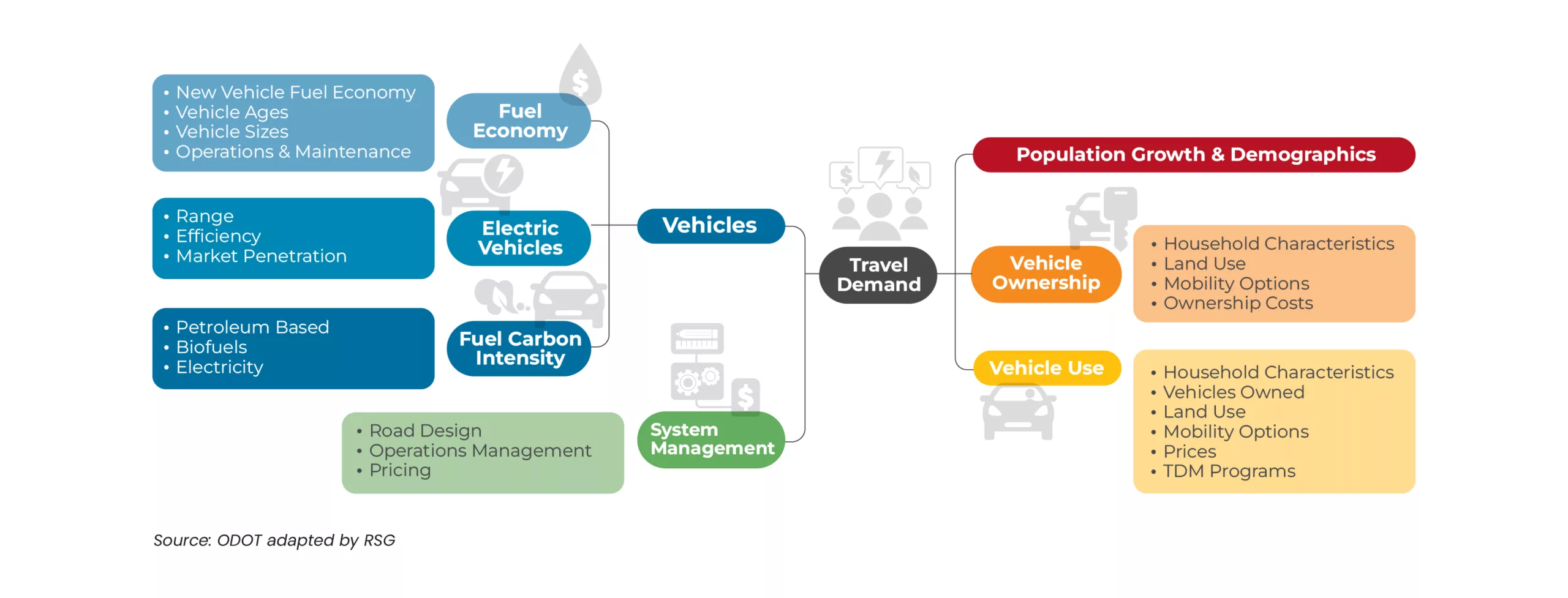
RSG’s Approach to System Dynamics Thinking and VisionEval
RSG roots much of our work in system dynamics thinking. This traces back to one of our founders, Dennis Meadows, whose groundbreaking research documented in The Limits to Growth changed how we view Earth’s systems. This perspective continues to shape our understanding of our place in the world and drives us to help develop and deploy cutting-edge tools like VisionEval. Our goal is to deliver solutions that are responsive to current needs and resilient to future uncertainties.
By developing and leading nationwide deployments of tools like VisionEval, our strategic transportation planning approach examines diverse scenarios and simulates the effects of various transportation policies, investments, and emerging technologies. By incorporating comprehensive data sources—economic, environmental, social, and technological—our tools equip clients with the insights necessary to make decisions that positively impact communities today and tomorrow.
For those wanting to explore how VisionEval can enhance your strategic planning efforts and address future transportation requirements, we invite you to reach out to our team to learn more about how we’re helping clients leverage this powerful, open-source tool recommended by FHWA and others.









